Choosing between commercial and personal auto insurance can significantly impact your coverage and costs. If you’re a business owner, entrepreneur, or someone who occasionally uses their vehicle for work, understanding the key differences between these two types of coverage is essential for making informed insurance decisions that protect your assets and comply with legal requirements.
What Is the Difference Between Commercial and Personal Auto Insurance?
The fundamental distinction between commercial vs personal auto insurance lies in how and why you use your vehicle. Personal auto insurance covers vehicles used primarily for personal activities like commuting to work, running errands, and recreational driving. Commercial auto insurance protects vehicles used for business purposes, whether owned by a company or used by individuals conducting business activities.
Personal auto insurance is designed for individual drivers and families who use their vehicles for everyday personal transportation. This coverage follows the driver and vehicle for personal use, providing protection during commutes, shopping trips, vacations, and other non-business activities. Most personal policies exclude coverage when the vehicle is used for commercial purposes, creating potential gaps for those who mix personal and business use.
Commercial auto insurance addresses the unique risks associated with business vehicle use. This coverage applies when vehicles are used to generate income, transport business equipment, carry passengers for hire, or conduct any commercial activities. Commercial policies typically offer broader coverage limits and specialized protections that personal insurance doesn’t provide.
When Do You Need Commercial Auto Insurance?
Understanding when commercial auto insurance becomes necessary helps prevent coverage gaps that could leave you financially vulnerable. Several key factors determine whether you need commercial coverage for your vehicle.
- Business Ownership of Vehicles represents the clearest indicator for commercial insurance needs. When your business owns or leases vehicles, commercial auto insurance is typically required regardless of how those vehicles are used. This includes company cars, delivery trucks, service vehicles, and any other automobiles registered under a business name.
- Revenue-Generating Activities require commercial coverage even when using personal vehicles. If you drive for rideshare services, deliver food, transport goods for sale, or provide services that require vehicle use, your personal auto policy likely won’t cover business-related incidents. Commercial coverage becomes essential for these activities.
- Employee Vehicle Use creates additional complexity for business owners. When employees drive company vehicles or use their personal cars for business purposes, appropriate commercial coverage becomes necessary to protect both the business and individual drivers from liability claims.
- Regular Business Transportation needs often exceed personal policy limits. If you regularly transport clients, carry expensive equipment, or use your vehicle as part of your business operations, commercial insurance provides the broader protection these activities require.
Main Coverage Differences B/W Personal and Commercial Auto
The coverage differences between personal insurance vs commercial insurance extend beyond basic liability protection to include specialized coverages that address unique business risks.
1. Liability Coverage Variations
Personal Auto Liability typically offers lower coverage limits suitable for individual drivers. Standard personal policies often provide state minimum liability requirements, which may not adequately protect business assets or address commercial liability exposures.
Commercial Auto Liability generally offers higher coverage limits and broader protection scope. Commercial policies often include Combined Single Limit (CSL) coverage that provides more flexibility in claim settlements and better protection against large liability claims that could threaten business operations. Want to Know more about liability defference read our blog on differecne between commercial insurance liability vs professional insurance liability.
2. Property Protection Differences
Comprehensive and Collision Coverage varies significantly between personal and commercial policies. Personal coverage focuses on vehicle repair or replacement based on actual cash value or agreed value for the individual owner. Commercial coverage often includes business equipment protection, cargo coverage, and specialized provisions for commercial vehicle modifications.
Business Equipment Coverage represents a major advantage of commercial policies. While personal insurance rarely covers business tools, equipment, or inventory transported in vehicles, commercial policies can include coverage for these valuable business assets.
Commercial vs Personal Auto Insurance Cost Analysis
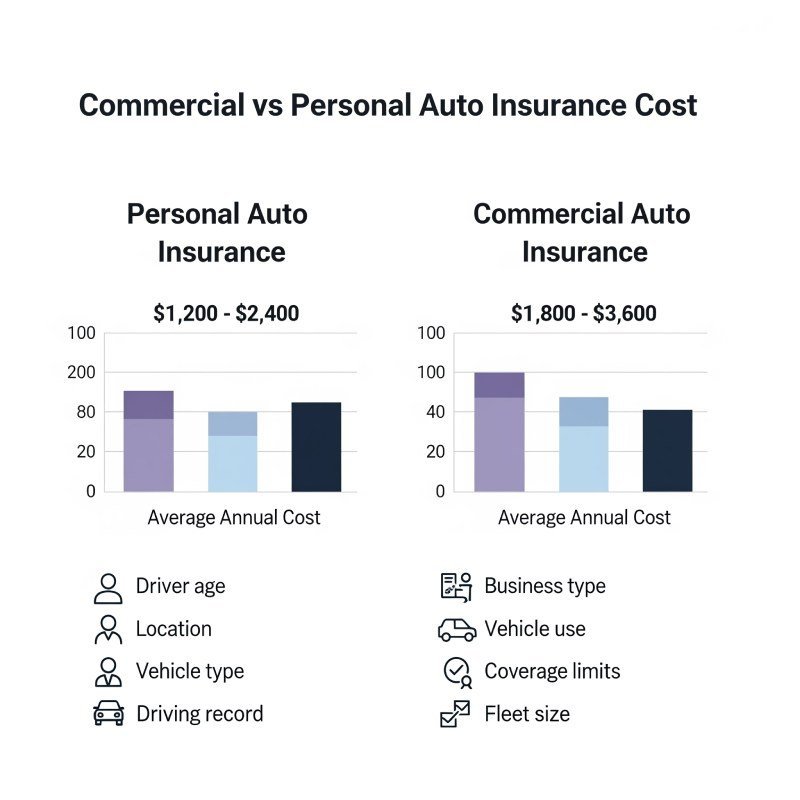
Understanding cost differences between car insurance business vs personal helps you budget appropriately and make informed coverage decisions. Several factors influence the price variation between these policy types.
| Coverage Type | Average Annual Cost | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Auto Insurance | $1,200 – $2,400 | Driver age, location, vehicle type, driving record |
| Commercial Auto Insurance | $1,800 – $3,600 | Business type, vehicle use, coverage limits, fleet size |
| Mixed Use Coverage | $1,500 – $3,000 | Percentage of business use, risk factors, coverage needs |
Cost Factors for Personal Insurance
- Individual Risk Factors primarily drive personal auto insurance costs. Your age, driving record, credit score, and vehicle type significantly impact premiums. Personal policies focus on individual driver behavior and vehicle risk characteristics to determine pricing.
- Usage Patterns affect personal insurance costs through annual mileage, commuting distance, and vehicle storage location. Lower mileage drivers often qualify for discounts, while high-mileage commuters may face higher premiums.
Cost Factors for Commercial Insurance
- Business Risk Assessment considers industry type, vehicle use patterns, and operational risks when pricing commercial coverage. High-risk industries like construction or delivery services typically face higher premiums than office-based businesses with minimal vehicle use.
- Fleet Characteristics influence commercial insurance pricing through vehicle types, driver pools, and safety programs. Larger fleets may qualify for volume discounts, while specialized vehicles or high-risk operations increase costs.
Is Business Auto Insurance More Expensive?
Commercial vehicle insurance is typically more expensive than personal auto insurance due to higher risk exposure and broader coverage requirements.
Car Insurance for Business and Personal Use
Many vehicle owners need coverage that addresses both business and personal use patterns. Understanding your options helps ensure adequate protection without unnecessary coverage gaps or redundant costs.
1. Dual-Use Scenarios
- Mixed-Use Vehicles present coverage challenges when the same vehicle serves both personal and business purposes. Personal auto policies typically exclude business use, while commercial policies can cover both business and personal activities under a single policy structure.
- Percentage-Based Decisions help determine appropriate coverage types. If you use your vehicle more than 20% for business activities, commercial coverage often provides better protection than trying to maintain separate policies or relying on personal coverage with business exclusions.
2. Coverage Solutions
- Commercial Policies with Personal Use often represent the most comprehensive solution for mixed-use situations. Commercial auto insurance can cover both business and personal use, eliminating the need for separate personal auto insurance.
- Business Use Endorsements may provide limited business coverage under personal policies, but these endorsements typically offer minimal protection compared to full commercial coverage. They work best for occasional business use rather than regular commercial activities.
Auto Insurance: Choosing the Right Coverage for Your Situation
Selecting appropriate auto insurance requires careful analysis of your specific needs, risk exposure, and budget considerations. Several key factors should guide your decision-making process.
1. Assessment Criteria
Vehicle Ownership Structure provides the clearest guidance for coverage selection. Business-owned vehicles almost always require commercial insurance, while personally-owned vehicles used occasionally for business may work with endorsements or separate coverage.
Revenue Dependency on vehicle use indicates commercial coverage needs. If vehicle problems would significantly impact your ability to generate income, commercial coverage with appropriate limits and additional protections becomes essential.
Risk Tolerance Evaluation helps determine appropriate coverage levels. Conservative business owners may prefer comprehensive commercial coverage even for minimal business use, while others might accept coverage gaps in exchange for lower premiums.
2. Decision Framework
Start with Vehicle Registration to determine basic requirements. Vehicles registered under business names typically require commercial insurance regardless of use patterns.
Analyze Usage Patterns to understand risk exposure. Regular business use, revenue generation, or employee access generally indicates commercial coverage needs.
Consider Financial Impact of potential claims on both personal and business assets. Commercial coverage often provides better asset protection for business owners and entrepreneurs.
Common Misconceptions About Auto Insurance Types
Several widespread misconceptions about commercial and personal auto insurance can lead to poor coverage decisions and unexpected claim denials. Understanding these myths helps ensure appropriate coverage selection.
Myth: Personal Insurance Covers Occasional Business Use
Reality: Most personal auto policies specifically exclude business use, even occasional activities. Personal auto insurance typically excludes business uses of a vehicle, making commercial coverage necessary for work-related driving.
Myth: Commercial Insurance Is Always Much More Expensive
Reality: Commercial auto insurance pricing is typically comparable to personal auto insurance, with exceptions for higher-risk operations. The cost difference often reflects broader coverage rather than excessive pricing.
Myth: You Need Both Commercial and Personal Policies
Reality: Most situations require only one type of coverage. Commercial policies can cover personal use, while personal policies typically exclude business activities entirely.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different industries face unique auto insurance challenges that influence coverage selection and cost considerations. Understanding industry-specific factors helps ensure appropriate protection.
High-Risk Industries for Auto insurance
- Construction and Contracting businesses often require specialized commercial coverage due to equipment transportation, job site risks, and contractor liability exposures. These industries typically face higher premiums but need comprehensive protection.
- Delivery and Transportation services face elevated accident risks due to high mileage, urban driving, and time pressures. Commercial coverage becomes essential for these businesses, often with additional cargo and customer liability protections.
- Professional Services like real estate, consulting, or healthcare may have moderate commercial insurance needs when vehicles are used for client visits or business travel. Coverage requirements depend on frequency and nature of business use.
Low-Risk Industries
- Office-Based Businesses with minimal vehicle use may work with personal insurance plus business use endorsements, though commercial coverage often provides better overall protection.
- Seasonal Businesses might benefit from adjustable commercial coverage that reflects varying usage patterns throughout the year.
Frequently Asked Questions
Business car insurance is typically more expensive than personal coverage due to increased risk exposure and broader coverage requirements. However, the cost difference varies significantly based on industry, vehicle use, and coverage needs. Some businesses with excellent safety records and minimal risk exposure may find commercial rates competitive with personal insurance.
Most personal auto policies exclude business use, making coverage void during commercial activities. Even occasional business use may result in claim denials. If you use your vehicle for any revenue-generating activities, commercial coverage or business use endorsements become necessary.
Typically, you only need one type of coverage. Commercial auto insurance can cover both business and personal use, eliminating the need for separate personal policies. This approach often provides better coverage and simplified management.
Ultimately understanding the differences between commercial vs personal auto insurance enables informed decisions that protect your assets and ensure adequate coverage. Even you need commercial coverage depends on how you use your vehicle, your risk tolerance, and your business operations.
Personal auto insurance works well for individuals who use vehicles exclusively for personal activities, while commercial auto insurance becomes necessary when vehicles are used for business purposes, owned by companies, or generate revenue. The cost difference between these coverage types often reflects the broader protection and higher limits that commercial policies provide.
Making the right choice requires honest assessment of your vehicle use patterns, risk exposure, and coverage needs. When in doubt, consulting with experienced insurance professionals helps ensure you select appropriate coverage that protects your interests without unnecessary costs or coverage gaps.
Remember that insurance needs evolve as businesses grow and personal circumstances change. Regular coverage reviews help ensure your auto insurance continues meeting your needs while providing the best value for your specific situation.